Clinical application guides
Main functions of Kinesiology Tape
Relief from pain and muscle fatigue.
Improves circulation and lymphatic drainage through superficial activation, reducing inflammation.
Corrects muscle function by reducing tension and strengthening weakened muscle.
Corrects joint misalignments.
Brings the body back to homeostasis.
Works with the body to allow and improve normal range of motion.
It can normalize length/tension relationships to create optimal strength.
Assists and improves tissue recovery.
Restores the homeostasis of epidermal tissues.
Reduces inflammation and pressure on mechanical receptors.
Hematoma (Contusion)
Contusions occur after a blow or repeated blows with a blunt object against a part of the body, causing rupture of the underlying muscle fibers and connective tissues, but without breaking the skin. A contusion can also be the result of a fall or the body hitting a hard surface.
Sometimes blood collects around damaged tissue, forming a clot (hematoma).
In more severe cases, bleeding and swelling under the skin can even lead to shock.
If the damage is extensive, there may be a fracture, dislocation, sprain, muscle strain and other injuries.
Contusions cause swelling, pain, reduction of range of motion in the area of the injury.
Broken blood vessels are responsible for the bluish discoloration.
The damaged muscle appears weak and stiff.
To control pain, bleeding and inflammation, hold the muscle in a gentle stretching position and use the RICE formula:
Rest: Protect the injured area from further damage by stopping play.
Protective equipment (i.e., crutches, harness) may also be used.
Ice: Apply ice wrapped in a clean cloth.
(Remove ice after 20 minutes).
Compression: Wrap the injured area in a soft bandage.
Elevation: Raise the affected area possibly above the level of the heart.
During the first 24 to 48 hours after the injury (acute phase), you will likely need to continue maintaining rest, ice, compression bandages, and elevation of the injured area to control bleeding, swelling, and pain.
While the injured part heals be sure to continue to exercise the uninjured parts of the body to maintain your overall fitness level.
After a few days, the inflammation should start to go down and the lesion will improve.
Indigestion
Indigestion is very common in adults ranging from rare to daily.
Indigestion can be caused by certain conditions of the digestive tract such as GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), peptic ulcer, cancer, or abnormalities of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
When these conditions improve or heal, the symptoms of indigestion also improve.
Most people with indigestion experience one or more of the following symptoms:
Sense of fullness during the meal: the person feels full immediately after starting the meal, unable to finish it.
Annoying sense of fullness after the meal: the person feels full after the meal and has the sensation that the food remains in the stomach for too long.
Epigastric pain: The epigastric area is located between the end of the chest and the navel.
The pain can be mild or severe.
Epigastric burning: annoying sensation of heat in the epigastric area.
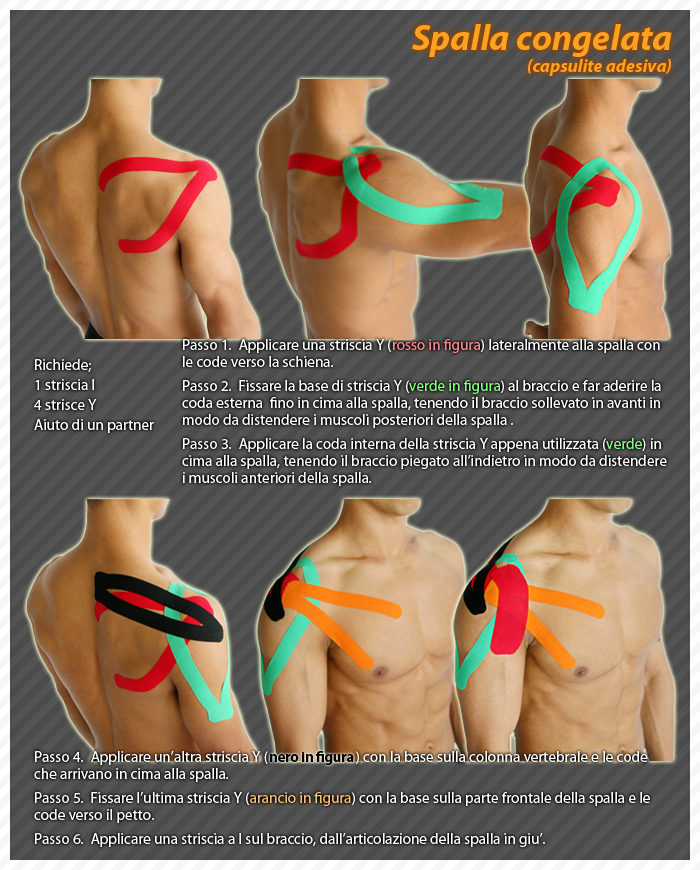
Frozen Shoulder
The causes of frozen shoulder are not fully understood.
The process includes thickening and contracture of the chasuble that encloses the shoulder joint.
Frozen shoulder affects approximately 10-20% of diabetic patients.
Other risk factors include: hypo- and hyperthyroidism, Parkinson's disease, heart disease, and surgery.
Frozen shoulder can also occur after the shoulder is immobilized for a period of time.
Some attempts to prevent frozen shoulder include mobilizing the shoulder early while recovering from an injury.
Symptoms
The pain due to frozen shoulder is often dull and worsens during attempts to move.
The pain is usually localized in the outer shoulder and deltoid.
The hallmark of the disorder is limited movement or stiffness of the shoulder.
The patient cannot move the shoulder normally. Movement is limited even if an outsider tries to move the patient's shoulder.
Treatment
Frozen shoulder usually heals on its own, although it can take two or three years.
Treatment aims to control pain and restore movement.
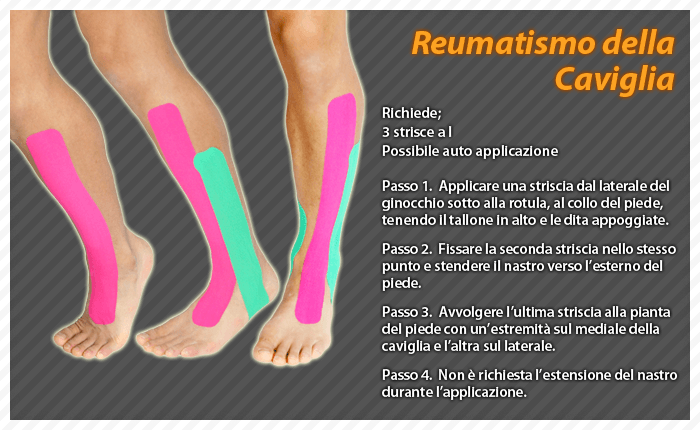
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease that attacks different joints throughout the body.
About 90% of people with rheumatoid arthritis develop symptoms related to the foot and ankle.
Symptoms typically appear first in the toes and ball of the foot, then spread to the back foot and ankles.
The exact cause of RA is unknown, although several theories exist.
Some concern the genetic nature, although environmental and chemical factors are also needed to trigger the disease.
In RA, the body's immune system attacks itself.
Instead of protecting the joints, the body produces substances that attack and inflame the joints.
Since RA affects the entire body, symptoms include fever, tiredness and loss of appetite.
Bumps develop around the joints, particularly in the elbow area.
Treatment
Exercise is key in AR. Your doctor or physical therapist recommend stretching and exercises to improve function and range of motion.
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia is a rare pain condition involving the intercostal nerves that innervate the chest muscles.
Patients with intercostal neuralglia experience banding pain around the rib cage.
The pain is usually intermittent and spasmodic.
The intensity varies based on different factors.
Patients may develop intercostal neuralgia as a result of nerve injury or as a result of a degenerative disease that compresses or damages the nerves.
Typically the pain is felt when breathing, coughing and laughing.
Exertional pain is also common.
Intercostal neuralgia manifests itself with tingling, numbness, itching, or pain, sometimes together.
In some cases the pain is felt as burning and like an electric shock.
Tennis Elbow (Epicondylitis)
Tennis elbow, or epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by strain and overuse.
It is no coincidence that the name derives from sporting activities such as tennis.
However, other sports and activities may put patients at risk.
Tennis elbow is an inflammation of the tendons that connect the forearm muscles to the outside of the elbow.
Forearm muscles and tendons become damaged from overuse by repeating the same motion.
This causes pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow.
Symptoms of tennis elbow develop gradually.
In many cases the pain starts out as bearable and then worsens over weeks and months.
There is no particular lesion linked to the onset of symptoms.
Common signs and symptoms are:
Pain or burning on the outside of the elbow
Weakening of grip strength
Symptoms often worsen with forearm activities, such as holding a racket, turning a key, shaking a hand.
Although the disease affects both arms, the dominant arm is more affected.
Approximately 80% to 95% of patients resolve the problem successfully without surgery.
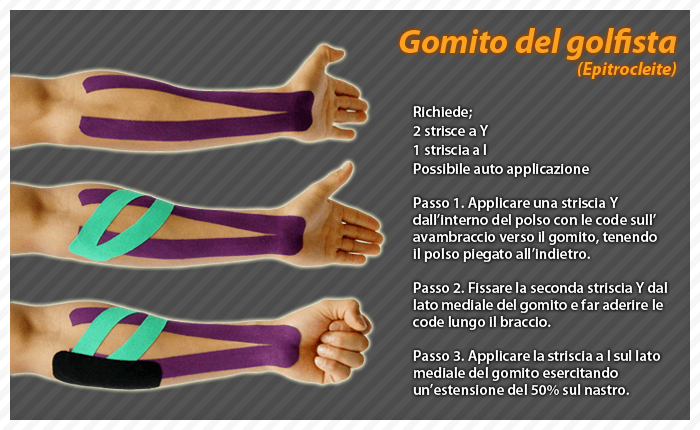
Golfer's elbow
At the top of the list of golfer injuries is golfer's elbow.
One of the best ways to avoid elbow problems is to strengthen your forearm muscles and slow down your swing so there is less shock in your arm when you hit the ball.
To avoid golfer's elbow, we suggest these simple exercises to strengthen your forearm muscles.
Squeezing a tennis ball
Squeezing a tennis ball for five minutes is a simple and effective exercise that will strengthen your forearm muscles.
Polso curl
Use a small dumbbell.
Lower the weight to the end of your fingers and then return the weight to your palm, followed by curling your wrist to lift the weight a few inches higher.
Do 10 repetitions with one arm and repeat with the other.
Backward wrist curl
Use a small dumbbell.
Place your hands forward with palms facing down.
Using your wrists, raise and lower the weight.
To limit movement to the forearm, hold the arm above the elbow with the other hand.
Do 10 repetitions with one arm and repeat with the other.
Thumb tendinitis (De Quervain Syndrome)
De Quervain tendonitis occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb become irritated or tight.
In fact, the term tendonitis refers to swelling of the tendons.
Thickening of the tendons can cause wrist pain and tenderness along the side of the thumb.
Signs of De Quervain Syndrome
Pain felt on the wrist on the thumb side.
It is the major symptom and can appear gradually or suddenly.
Pain from the wrist can radiate to the forearm and worsens especially when using the hand and thumb.
The most painful movements coincide with grasping objects or rotating the wrist.
It is possible to appreciate swelling on the wrist on the thumb side.
The swelling may coincide with a fluid-filled cyst in the area.
Patients report a "catching" or "catching" sensation of the thumb during movement.
Pain and swelling make it difficult to use your wrist and thumb.
Numbness may be felt behind the thumb and on the index finger.
The cause is the nerve that rests on the tendon sheath becoming irritated.
The goal of treating De Quervain syndrome is to relieve pain caused by irritation and swelling.
Calf swelling
Calf injuries due to straining lead to swelling.
There may be a bruise.
When muscle fibers break down, a tear can occur.
If the calf muscle is partially or completely torn, the symptoms are bruising, swelling, and pain.
The tear is sometimes noticeable when the muscle sticks out as a bump.
Muscle Cramps
A cramp is a forced, involuntary contracture of a muscle that does not relax.
Cramps can affect any voluntary muscle.
Muscles that affect two joints are more prone to cramps.
The most commonly affected muscle groups are:
Posterior leg/calf (Gastrocnemius)
Hamstrings (Ischiocrurals)
Front of the thigh (Quadriceps)
Cramps in the feet, hands, arms, abdomen and along the rib cage are also very common.
Although the exact cause of muscle cramps is unknown (idiopathic), some researchers think that inadequate stretching and muscle fatigue lead to abnormal conditions of the mechanism controlling muscle contraction.
Other factors may be involved such as poor conditioning, training or working in extremely hot environments, dehydration and mineral (electrolyte) depletion.
Treatment
Cramps normally resolve without medical support.
Stop any activity that triggered the cramp.
Lightly stretch and massage the affected muscle, keeping it stretched until the cramp goes away.
Apply hot to tense muscles or cold to relax them.
Prevention
To avoid cramps it is preferable to be in good physical condition.
Do regular flexibility exercises before and after training to stretch the most involved muscle groups.
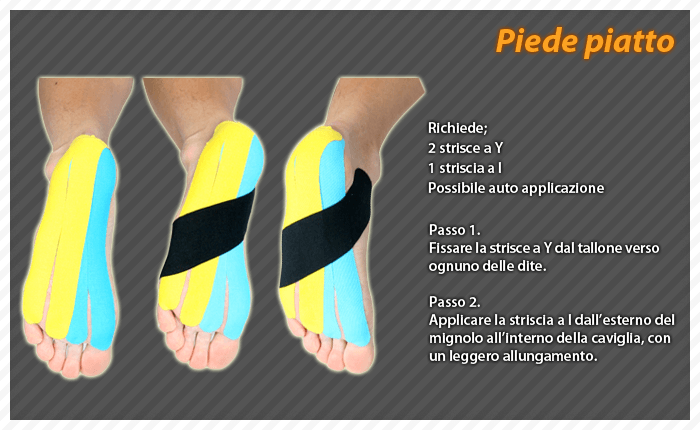
Flatfoot
Flat foot is the condition in which the internal longitudinal arch of the foot collapses and comes into contact with the ground.
In children and infants the longitudinal arch is not developed and flat feet are normal.
In some individuals the longitudinal arch never develops.
Flat feet may be associated with pronation, which is an inward slope of the ankle bones.
Common symptoms of flat feet are:
Flat appearance of one or both feet
Irregular footwear and shoes that collapse inward
Leg pain
Pain inside the ankles
Swelling of the ankles
Foot pain