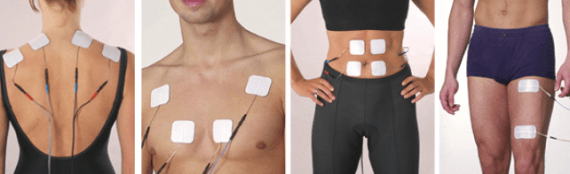
ELECTROSTIMULATION
FIELDS OF USE
Electrostimulation is a particular method used for various objectives:
1. in the medical field - for pain relief and anti-inflammatory therapy
and for post-injury functional re-education
2. in the aesthetic field - for localized weight loss and lymphatic drainage.
3. in the sports field - for muscle strengthening and recovery.
HOW STIMULATION WORKS
The device generates a type of current characterized by very specific waveforms.
The generated current passes through the cables and reaches the electrodes placed in contact with the skin.
The passage of electric current between the positive electrode and the negative electrode
it is transferred to the body depending on the waveform used, resulting in different effects.
EFFECTS OF STIMULATION
Depending on the type of current delivered to the body, different effects are obtained:
Analgesic current - pain-relieving effect: blockade of nerve impulses
that involve the sensation of pain.
Aesthetic current - slimming effect: lipolysis and drainage of retained liquids.
Sports current - relaxing and toning effect: increased circulation and warming
of the affected area; muscle contractions of varying intensity.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Electrostimulation used on healthy people has no particular contraindications, except in the case of an exaggerated use of the strongest muscle stimulation programs which can lead
to fatigue and muscle pain.
At the same time, the use of electrostimulation as therapy can be very frequent,
even more than the recommended programming (e.g. TENS), but the sessions must still be spaced a few hours apart to allow the stimulated area to acquire the positive effects produced by the application; too frequent use of these programs, in fact,
it may not have better results than normal programming, making it useless.
In general, however, for some cases it is not possible or it is inadvisable to use this type of therapy:
CONTRAINDICATIONS (avoid application or, in any case, keep away
from risk areas)
1. Presence of pacemaker
2. Heart problems (pathologies, arrhythmias...)
3. Front area of the neck
4. Lateral surface of the neck
5. Pregnant women (abdomen and lumbosacral area)
6. Areas with skin lesions, mucous membranes, alterations in local sensitivity, processes
infectious, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis)
7. Near metal prostheses (especially for monophasic currents such as iontophoresis)
8. On areas affected by tumors or stones (liver and kidneys)
9. Severe liver or kidney failure
10. Arterial hypertension
11. Hormonal imbalances
12. Metabolic disorders
13. Taking anticoagulants
14. Neurological disorders
15. Severe varicose veins
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE STIMULATED ZONES
The effects of the stimulation are linked to the value of the parameters used
and the positioning of the electrodes on the skin.
As far as muscle stimulation is concerned, there are zones
in which the concentration of nerves is greater therefore the electric field produced
from the passage of the current between the positive and negative electrodes it must include these points of greatest sensitivity to obtain optimal muscle contraction.
In the case of aesthetic treatments, however, to dissolve subcutaneous fat
it is necessary that the stimulation remains on the surface and includes, in addition to the layer to be eliminated,
also the vessels of the local circulation to facilitate the drainage of the released substances.
TENS (pain therapy) is also applied to the area of need like beauty treatments;
however, the particularity of the parameters means that the stimulation affects the sensitive nerves, blocking the transmission of painful impulses.
TENS
The term TENS (abbreviation for Transcutaneus Electrical Nerve Stimulation) refers to electrostimulation with low voltage analgesic impulses.
Diphasic pulses are generally used, both to avoid electrochemical phenomena
than the onset of habituation.
Different TENS application techniques can be distinguished, connected to different mechanisms of action.
The analgesic effect can in fact be traced back to:
· To an inhibition of nociceptive stimuli at the spinal level ("gate control theory");
· To the activation of descending inhibitory systems;
· To the release of endogenous opioid substances;
· To a block of nociceptive impulses;
There are two main techniques, conventional TENS and electroacupuncture-type TENS.
Conventional TENS is characterized by stimuli of short duration, mild intensity and relatively high frequency. It works by stimulating the larger fibres, triggering the gate phenomenon ("gate control theory").
The TENS type of electroacupuncture is characterized by pulses of longer duration, higher intensity and lower frequency. It works mainly through
the release of endogenous morphine-like substances.
INDICATIONS:
· Chronic pain;
· Traumatic lesions of a peripheral nerve;
· Cervical and lumbosacral pain;
· Artrite reumatoide;
· Causalgia;
· Scapulohumeral periartitis;
· Post-herpetic neuralgia;
· Phantom limb pain;
· Pain from root involvement (cervicolumbalgia, lumbosciatica, crualgia).
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- Pace maker carriersPregnancy